Is Apple Pay safe? How it works, what’s protected, and what to watch out for

Over 90% of retailers in the United States accept Apple Pay. As the payment method’s popularity only grows, you may be wondering—is Apple Pay safe to use?
The answer is a definite “Yes.” The merchant is never given your card number, even Apple doesn’t have access to it. Instead, Apple Pay uses a tokenization method to process transactions. That means a code, not your card number, is transmitted when you pay.
Additionally, users are required to pass authentication using facial recognition, Touch ID, or a device passcode to authenticate payments. And although nothing is perfect, Apple Pay is safer to use than many other methods, as long as you enable its safety features.
How Apple Pay works
Apple Pay is a built-in iOS feature accessible through the Wallet app. Although the Wallet app is pre-installed on most iPhones, you can also download it from the App Store.
To enable the feature, all you need to do is add a card to the Wallet. In addition to credit and debit cards, you can also add prepaid or Apple Cards.
Most banks require identity verification to confirm that you’re the legitimate cardholder before it’s active via Apple Pay. You may be required to enter a code, click a verification link sent to your email, or verify via your bank app. Once the card is verified, you will see it in your Wallet. If you add several cards, you’ll be able to choose the default one.
Once everything is set up, you can use Apple Pay wherever contactless payment is accepted— simply hold your device near a payment terminal. Many online shops allow checkout with Apple Pay as well. It can also be used for peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions to send money to other Apple users using the Apple Cash feature.
But how secure is Apple Pay and is it a good option for regular purchases?
While no service is completely immune to scams, the following features make Apple Pay one of the best payment methods to use both online and offline:
Tokenization and device-specific numbers
Tokenization is a robust security feature which ensures that your card number isn’t stored on your device and Apple Pay servers and isn’t shared with merchants during transactions.
Instead, Apple Pay replaces it with a unique, randomly generated device-specific number called the Device Account Number (DAN) or the Device Primary Account Number (DPAN). The DAN/DPAN is securely stored in the Secure Element (a specialized chip in your device isolated from the OS and apps).
When you use Apple Pay, it generates a one-time security code and sends it to the payment terminal along with the DAN. The payment network authorizes the transaction with your bank, but never gets access to your card number.
The merchant only sees the payment amount. Some may also see your name or billing info (if required in their system), but never any sensitive financial details.
Payment authentication
For every transaction you initiate, Apple Pay uses authentication to confirm it’s really you. You can verify your identity using Touch ID (fingerprint), Face ID (facial recognition), or a passcode.
Authentication is required before holding your device near a payment terminal and ensures that unauthorized individuals aren’t able to pay even if they get hold of your device.
Apple Pay doesn’t allow disabling authentication for standard transactions which greatly differentiates it from many other contactless payment methods.
What happens if your device is stolen?
Because of payment authentication, no one but you is able to make transactions—even if they have your device.
Additionally, you can remotely disable Apple Pay via the Find My app in case your device is lost or stolen. To do that, open the Find My app on another Apple device you own, go to the Devices tab, select the device in question, tap “Lost Mode”, and follow the prompts. Alternatively, you can sign in to iCloud with your Apple ID and use the Find Devices app there. Both methods will disable Apple Pay automatically.
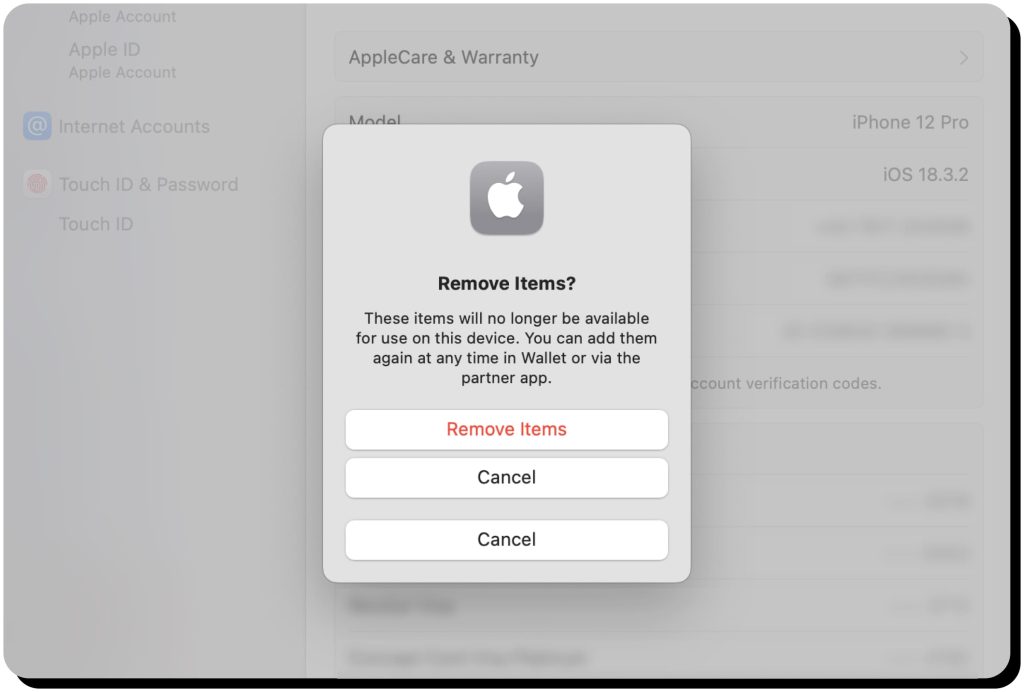
For extra assurance, you can even manually remove cards from Apple Pay via your Apple account. Go to Devices and choose the necessary one. Then go to the Wallet & Apple Pay section and click “Remove Items.”
Note that you can re-enable Apple Pay once you recover your device and pass identity authentication.
Is Apple Pay safer than cards or PayPal?
Credit and debit cards vs. Apple Pay
Even though traditional cards are still widely used, they are more vulnerable to security risks than Apple Pay.
For one, they reveal a lot more of your personal and financial information to merchants, including your full card number and name. This information can easily be breached and stolen, exposing you to numerous threats.
Additionally, cards are easier to abuse if someone gets hold of them. Since they rely on weak authentication methods like PINs (if any at all for contactless transactions), a thief can make purchases without verifying that they are the actual owner.
In contrast, Apple Pay never reveals your card details to a merchant and requires authentication every time you want to make a purchase. It can also be remotely disabled in case you lose your device.
PayPal vs. Apple Pay
Though both are great options, PayPal and Apple Pay are quite different in how they operate and handle user data.
First, you can’t pay with PayPal in physical retail stores. However, it’s commonly used for recurring payments (subscriptions), while Apple Pay is usually not supported. PayPal is also more convenient for P2P transfers.
Second, even though the platform has generally strong security features, payment authentication is optional and usually relies on account login. Two-factor authentication can be enabled, but it’s also optional. This means that anyone who has login credentials to your account can make purchases using your PayPal.
It also collects and stores way more user data both for internal and third-party use. On the contrary, Apple Pay is more privacy-focused, collects the very minimum of your data, and is a better choice if you want to keep your details private.
On the other hand, PayPal offers better buyer protection, which is especially valuable when buying from unknown sellers. It allows you to dispute a transaction and covers many physical goods and digital services. Apple Pay, in turn, doesn’t have its own protections and relies on those of a linked card.
When Apple Pay is more secure
Apple Pay is generally considered the best payment option both online and offline due to its robust security features. It’s especially beneficial to use it:
- For in-store purchases
- For online shopping on Apple devices
- In case there’s a risk of your device getting lost/ stolen
- If you’re concerned about your privacy
Limitations of Apple Pay
While overall a fast and convenient payment method, there are a few Apple Pay cons:
- You’re dependent on your device. In case the battery dies, you’ll need a physical card.
- It isn’t accepted by every retailer, both online and offline.
- It isn’t available everywhere worldwide. Some regions don’t have access to Apple Pay at all.
- Not all banks support Apple Pay and some cards may not be eligible for setup.
- It doesn’t support recurring payments and subscriptions.
- It doesn’t provide its own buyer protection and dispute resolution.
Apple Pay is an excellent choice for convenience and security, as the benefits far outweigh the disadvantages. Ultimately, it’s up to you to decide what payment method works best based on your needs and concerns.
How to use Apple Pay securely
Apple Pay is very secure due to its built-in features that safeguard your information. However, there are additional practices you can follow to ensure maximum protection:
- Set strong device passcodes: In case you opt for passcodes instead of biometric authentication, make sure they are complex and difficult to guess. If someone is able to unlock your iPhone, they could create a new biometric profile, which would lead to unauthorized transactions.
- Set up Apple Pay only on trusted devices: Make sure you have the latest OS version and avoid jailbreaking as it can compromise security features.
- Avoid adding new debit cards to Apple Pay on public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-fi typically lacks encryption and your data can be intercepted.
- Regularly monitor your bank activity: Review your bills and check if you recognize all the charges in the payment history.
- Enable the Find My feature so that you can disable Apple Pay in case your device is lost.
- Stay alert for scams: Stay educated on the latest scam techniques so that you don’t fall for fake Apple support communications, phishing emails, and other attacks that may compromise your financial data.
How Onerep helps minimize scam risks
Apple Pay does a great job of keeping your personal information private. However, not all services you frequently use do the same. Numerous platforms and sites, that are part of our daily routine, collect data and share it with third parties. One such party is data brokers, who, in turn, make that data easily available online.
Data brokers publish your name, address, contacts, income, credit score range, occupation, and many other sensitive details. Having such private information easily searchable online makes you an easy target of phishing, financial fraud, Apple support impersonation scams, and other threats.
Onerep safeguards your identity by removing your personal info from 230 data brokers. The service regularly scans the sites and sends opt-out requests as soon as it finds your exposed details. By continuously monitoring data brokers and enforcing your right to privacy, Onerep greatly reduces your online exposure and makes your private information ungooglable.
Using a data removal service like Onerep in addition to a privacy-oriented service like Apple Pay helps you keep your sensitive data private and prevent it from being weaponized in scams and identity theft.
FAQS
How secure is Apple Pay?
Apple Pay is the safest payment method to use. It doesn’t provide card numbers to merchants and it doesn’t store them on your devices or Apple servers. Apple Pay also requires authentication every time you pay, so no one else can use your device to make transactions unless they know your passcode.
Is Apple Pay safer than a credit card?
Yes, Apple Pay is safer than using a credit card. Primarily, because Apple Pay doesn’t expose your card number and other personal information like cards do. Cards are also easier to abuse if they are stolen while Apple Pay verifies your identity for every transaction.
Is Apple Pay safe from scams?
Apple Pay is protected from many scams like card skimming and data interception due to tokenization and identity authentication. However, it can’t protect you from unsecured websites and phishing. It’s up to you to make sure you’re using Apple Pay only with trusted retailers.
Does Apple Pay have buyer protection?
No, Apple Pay doesn’t offer buyer protection. Protection and dispute rights depend on your card issuer.
Is Apple Pay or PayPal safer?
Apple Pay is generally safer than PayPal. Unlike Apple Pay, PayPal collects and stores user data, and its payment authentication process isn’t as robust.
How safe is Apple Wallet?
Apple Wallet is very safe. It stores payment credentials in the Secure Element, but it never stores card details. Also, access to the Wallet is protected with identity verification to prevent unauthorized use in case your device is stolen.
What are the cons of using Apple Pay?
Main Apple Pay cons are that it’s not accepted by some retailers and in some countries. You also depend on your device and need cash or a card in case your battery dies.
Is Apple Pay safe from hackers?
Yes, Apple Pay is generally safe from hackers. It doesn’t store the account numbers on the phone or the Apple servers. Even if your device is compromised, payments require biometric authentication or a passcode. You can also disable Apple Pay remotely if you lose your device.
Is Apple Pay safer than a debit card?
Yes, Apple Pay is safer than a debit card. Apple Pay doesn’t expose your card number to the merchant. Debit cards can be used if they are stolen but Apple Pay is protected by identity authentication.
Is Apple Pay a safe app to store payment info?
Apple Pay is safe to add your cards to as it doesn’t store card numbers or other payment information. All payment data is stored in the Secure Element and never shared with Apple or third parties.





Mark comes from a strong background in the identity theft protection and consumer credit world, having spent 4 years at Experian, including working on FreeCreditReport and ProtectMyID. He is frequently featured on various media outlets, including MarketWatch, Yahoo News, WTVC, CBS News, and others.