Is Proton Mail safe? The 2025 guide to encrypted email and online privacy

Proton Mail is widely considered one of the safest email providers in 2025 due to robust security and privacy features. These include end-to-end encryption, zero-access storage, two-factor authentication, and open-source, independently audited code. Your messages are encrypted on your device, stored in unreadable form on Proton’s servers, and can’t be decrypted by Proton staff or hackers if the servers are compromised.
Still, no platform is completely unvulnerable. Some personal details aren’t fully protected by encryption, and Proton may be legally compelled to share them with authorities. Additionally, device-level risks such as phishing, malware, or compromised accounts remain outside Proton’s control.
What is Proton Mail?
Proton Mail is a secure, privacy-first email provider founded in Switzerland in 2014 and operated by Proton AG, a Swiss corporation whose primary shareholder is the Proton Foundation, a Geneva-based nonprofit.
The company was first conceived of by a group of scientists at CERN – the European Organization for Nuclear Research – who believed people should be able to communicate without their data being collected or sold.
Proton Mail is available via web browsers and as a standalone app for Android, iOS, Windows, Mac, and Linux. There’s also Proton Bridge, which lets you use Proton Mail with popular email clients such as Outlook, Apple Mail, and Mozilla Thunderbird.
It’s all part of an entire Proton ecosystem that also includes:
- VPN: Virtual Private Network
- Drive: File storage and sharing
- Calendar: Privacy-first calendar
- Pass: Password manager
- Wallet: A self-custodial Bitcoin wallet
- Authenticator: Two-factor authentication app
- Simple Login: A service that allows you to send and receive emails anonymously by creating aliases
- Standard Notes: A privacy-focused notetaking app
- Lumo: Proton’s confidential AI chatbot
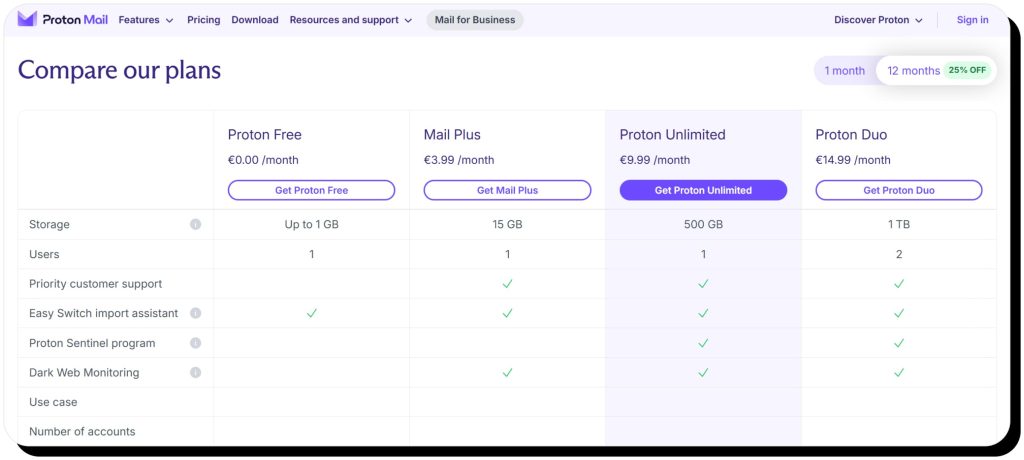
Most of these are available as standalone services with free and paid tiers, but you can also bundle services. Additionally, Proton Mail has a 30-day money-back guarantee and offers family and business plans. However, in this guide, we’ll focus on individual plans.
How secure is Proton Mail?
Proton Mail is highly secure due to end-to-end and zero-access encryption as well as features like open-source and independently audited code, self-destructing messages, hide-my-email aliases, and Tor Network access.
Encryption
Proton Mail comes with zero-access and end-to-end encryption (E2EE) out of the box.
- E2EE means only the sender and recipient can read the contents of an email.
- Zero-access encryption means Proton cannot read that data at rest.
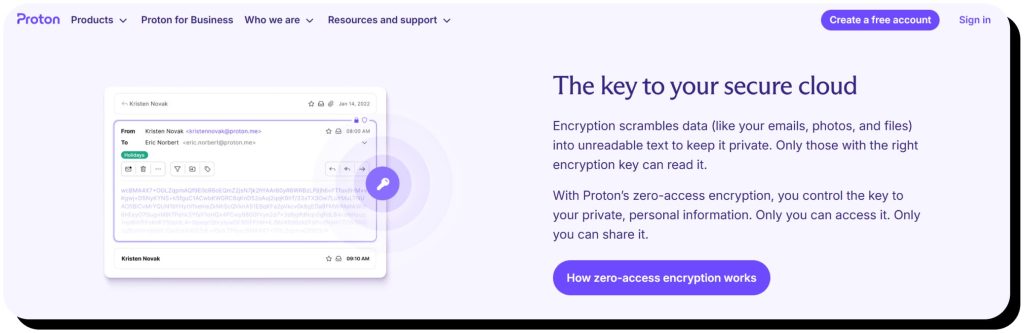
However, end-to-end encryption is only automatic when an email is sent between Proton Mail users. If you’re sending an email to a non-Proton Mail user, such as to a Gmail address, Google will be able to read it by default. However, there is a workaround: password-protected emails. Here’s how it works with Gmail:
- Send a password-protected email to a Gmail address.
- Use a secure method like Signal or a phone call to share the password.
- Google will not be able to read the email.
- If the recipient replies to your original email, their response will also be encrypted.
Keep in mind that this only works for emails you send from Proton Mail. If a Gmail user sends a new email to you, it won’t arrive encrypted. However, Proton Mail will encrypt it once it resides on the server, so it won’t be readable in the event of a data breach.
Open-source and independently audited code
Open-source code means that Proton Mail’s codebase is available to the public, which enables anyone to inspect it and find hidden issues before hackers can exploit them. It also means that users can verify that there aren’t any hidden data-collection mechanisms or undisclosed tracking. Moreover, Proton Mail has independent experts audit the code and verify the service is secure.
Two-factor authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to keep bad actors from accessing your Proton Mail account. Proton Mail supports two different types of 2FA:
- Authenticator app, including Proton’s own Authenticator
- Security key, either via a platform such as Windows Hello or Apple Touch ID, or via a physical USB security key (FIDO U2F)
Hide-my-email-aliases
This unique feature allows you to create email aliases: fake emails that you can use to sign up for non-essential services or otherwise share with anyone you don’t want to know your true address. Emails sent to your alias are automatically forwarded to your primary email, and if your aliases are ever compromised, you can instantly deactivate them.
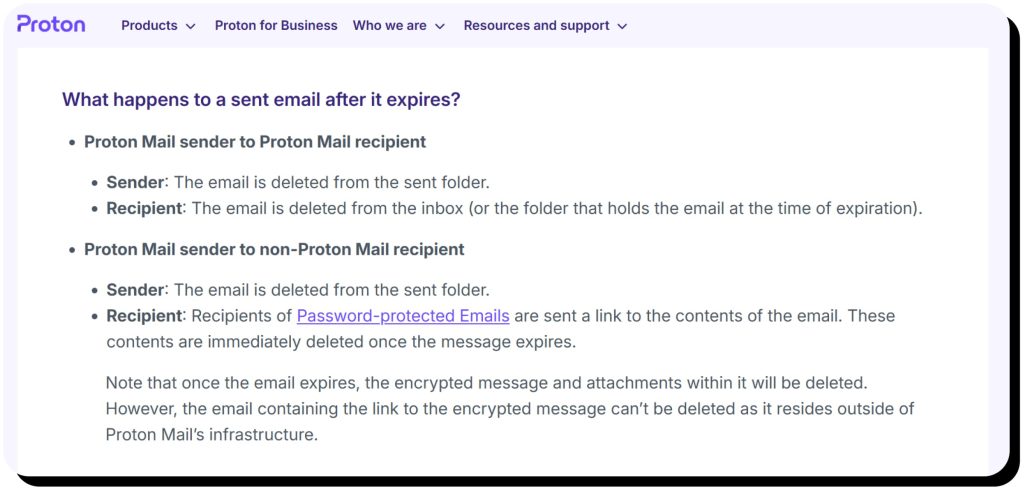
Self-destructing messages
As the name implies, this Proton Mail feature allows you to set an expiration for emails you send, so they’ll automatically delete at that date and time. It only works for end-to-end encrypted emails between Proton Mail users and password-protected emails sent to non-Proton Mail users. Note that paid Proton users can also set expiration dates for emails they receive.
Tor Network access
Tor is a secure network that allows users to browse the Internet anonymously. It’s often used by people who need supreme security – such as journalists and activists, especially in countries that don’t have freedom of speech. When you use Tor with Proton Mail, no one can easily identify you or your location. In fact, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can’t even tell you’re using Proton Mail.
However, Tor can be slow, and though it provides the greatest level of security, it might be overkill for most users. Unless you deal with highly sensitive data, you might be better off using Proton Mail with Proton VPN to protect your anonymity.
What Proton Mail can (and can’t) protect you from
Proton Mail offers excellent security and privacy that help protect your data, but like any email platform, it can’t protect you from every possible threat out there.
Proton Mail CAN protect you from:
- Interception of emails during transmission
- Server-level data breaches (since email content is encrypted)
- Email-based identity theft via strong 2FA
- Mass tracking, as Proton Mail doesn’t add trackers or ads, reducing behavioral data collection
However, Proton Mail CAN’T protect you from:
- Malware or spyware on your device, which could be used to log your keystrokes, steal your password, and access your account
- Phishing attacks impersonating Proton Mail
- Compromised recipient email accounts (if your recipients’ emails are hacked, messages sent to them may be leaked)
Common concerns and criticism
Despite its reputation as a secure, privacy-first email platform, Proton Mail does face some concerns and criticism. However, it’s important to note that the following concerns don’t compromise Proton Mail’s integrity but reflect real-world privacy challenges.
Law enforcement requests
In 2021, Proton Mail logged the IP address and device information of a French climate activist after being legally compelled to by the Swiss government. Proton explained that the company can be forced to collect such user data under Swiss law, but that they weren’t able to turn over any messages because their encryption worked. Proton also emphasized the option to use Tor to ensure complete anonymity when using Proton Mail.
In 2024, Proton was legally compelled to share a recovery email address for the primary Proton Mail address a Spanish activist used for their Wire account. It was an iCloud email address, so authorities were able to get the user’s identifying information from Apple, and the activist was arrested.
These cases illustrate how legal mechanisms can be used to force even the most secure providers to share user data, underscoring the need to take extra measures to protect your identity.
Credential harvesting
Scammers and hackers employ multiple strategies to harvest your login credentials so they can access your online accounts, including:
- Phishing and smishing
- Malware and spyware with keylogging
- Data breaches released on the dark web
Hackers also find your personal information on data brokers – specifically, people-search sites. These sites collect sensitive data such as your name, birthday, address, email address, phone number, relatives, and other private details. This information can then be used to guess your password or answer security questions to access your account.
If you use personal information in your login credentials or reuse them across different services, scammers might be able to guess or steal them. In case they do, there’s not much Proton Mail can do to stop them from logging into your account.
Metadata and subject lines
Proton Mail provides end-to-end encryption for email content, but the OpenPGP standard it adheres to does not offer E2EE for the header packet that includes email addresses and subject lines. For that reason, you should never include sensitive information in your subject lines.
Proton Mail vs. Gmail
So, how does Proton Mail stack up to Gmail? Here’s a breakdown of key features.
Encryption
Proton Mail offers true end-to-end encryption out of the box, while Gmail does not – it only encrypts data in transit (TLS), which means Google can read your messages. Gmail did recently introduce end-to-end encryption for businesses, but experts say it’s not true E2EE because organization administrators have the keys and can therefore access email messages.
Privacy Policy
Proton Mail features zero-access encryption, meaning even Proton cannot read the content of your emails. The company also doesn’t track you when you use other services like VPN or Calendar. Proton doesn’t have ads in general.
As for Google, even though it doesn’t use the content of your messages for ads, it still tracks you massively across its services and creates detailed behavioral profiles.
Accessibility
Free Gmail accounts come with 15GB of storage – 15 times more than Proton Mail’s free tier. As a Google product, Gmail also boasts a much larger app ecosystem than Proton. In addition, far more users are familiar and comfortable with Google’s products than Proton’s.
The bottom line? Google’s massive ecosystem gives Gmail the edge for seamless integration and universal acceptance, but Proton Mail is the better choice for privacy-conscious users.
So, is Proton Mail worth it?
Yes, Proton Mail is worth it if:
- Privacy is a top priority for you
- You deal with sensitive communications
- You want to reduce data tracking and behavioral profiling
- You’re a journalist, activist, or privacy-conscious professional
That said, you might be better off with Gmail if you need deep integration with Google Workspace tools, maximum storage space for free, or if you heavily rely on third-party app integrations within Google’s ecosystem. Of course, you can unlock more storage and capabilities – such as Proton Drive – with a paid Proton Mail plan, so be sure to carefully weigh your options and priorities before deciding.
How to maximize safety when using Proton Mail
Follow these best practices to maximize safety when using Proton Mail:
- Use Tor or Proton VPN to mask your IP address
- Use Proton aliases for non-essential sign-ups
- Never include sensitive information in subject lines
- Encrypt emails to non-Proton Mail contacts
- Don’t create a recovery email address
- Don’t use identifying information (name, birthdates, graduation years, etc.) in your Proton email address or passwords
- Use self-destructing messages when sending sensitive information
- Use Proton Contacts (built into Proton Mail) to encrypt your contacts’ data
- Use a strong, unique password and enable 2FA
- Check authentication logs in Proton Mail settings to identify suspicious logins (you can also log out of other sessions)
- If you use the Proton Mail iOS app, enable AppKey for another layer of protection to access Proton data on your device
- Scan your devices for malware and spyware regularly
How Onerep helps protect your privacy
People-search websites collect and publish online an awful lot of your personal information, including full name, contacts, relatives, DOBs, graduation year, interests, and more. These details can be used by scammers to guess your credentials and answers to security questions. In a more common scenario, this data is used to create convincing phishing emails that trick you into revealing more info and compromising your accounts.
Onerep helps prevent these threats by automatically removing your personal data from 230 people-search sites. Then, it monitors each website to ensure your information isn’t republished; if it is, the removal process starts again. In this manner, Onerep stops your personal info from being exposed online, keeping it out of the hands of bad actors and helping protect your privacy.
FAQs
Is Proton Mail encrypted?
Yes, Proton Mail has zero-access and end-to-end encryption between its own users. It even allows you to send end-to-end encrypted messages to non-Proton Mail users via password-protected emails.
Can Proton Mail be hacked?
While any online platform can theoretically be hacked, there are no verified Proton Mail data breaches. All known Proton Mail exploits are due to human factors, such as falling victim to phishing scams. Additionally, Proton encrypts data at rest, so the content of your messages wouldn’t be compromised even if the platform was hacked.
What are the disadvantages of Proton Mail?
The primary disadvantages to Proton Mail are limited free storage (1GB) and a minimal app ecosystem compared to alternatives like Gmail/Google. If you need more storage or access to massive ecosystems, these could be reasons why you should not use Proton Mail.
Is Proton Mail secure?
Yes, Proton Mail is a secure email platform that uses zero-access and end-to-end encryption, which means even Proton itself cannot read the content of your emails.
Is Proton Mail good for free users?
Proton Mail might be a good option for free users who do not need to store many emails, as storage is capped at 1GB on the free plan.
Does Proton Mail have good reviews?
Proton Mail reviews are generally positive from media outlets, which cite the service’s high security levels and ease of use. Proton Mail has even been named TechRadar’s #1 best email provider for privacy. That said, the service only has a 2.3-star rating on Trustpilot, where Proton Mail complaints often center around billing and customer support issues.





Mark comes from a strong background in the identity theft protection and consumer credit world, having spent 4 years at Experian, including working on FreeCreditReport and ProtectMyID. He is frequently featured on various media outlets, including MarketWatch, Yahoo News, WTVC, CBS News, and others.